Of the many scientifically proven benefits to beekeeping, two stand out as especially important to building sustainable livelihoods. The first is economic, resulting from the sale of bee products. The second is ecological, comprising the service bees do the environment by pollinating flowers. It is in fact estimated that bees pollinate one out of every three food items that we consume daily.
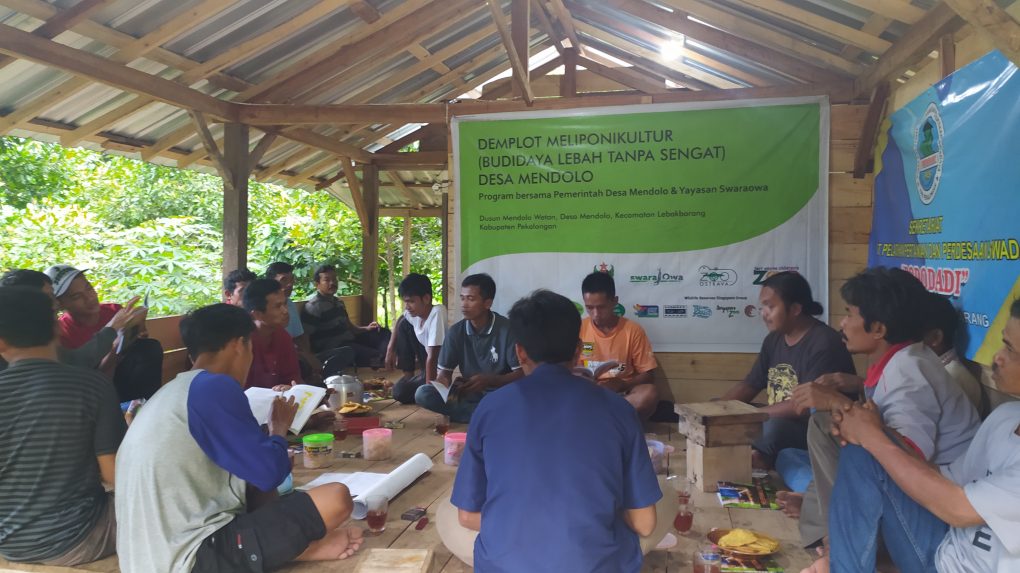
Situated near the rainforests that the Javan gibbon wild habitat, the residents of Sawahan- Mendolo Village in Central Java have a crucial role to play in securing the future of this endangered primate. The men in this village have now enthusiastically embraced the idea of rearing stingless bees for honey, an activity known as meliponiculture. Having mostly hunted for honey in the forest in the past, keeping stingless bees in their gardens has both added to their income and made them more economically self-sufficient. This has strengthened our belief in the potential that meliponiculture has as a means of livelihood that promotes conservation.
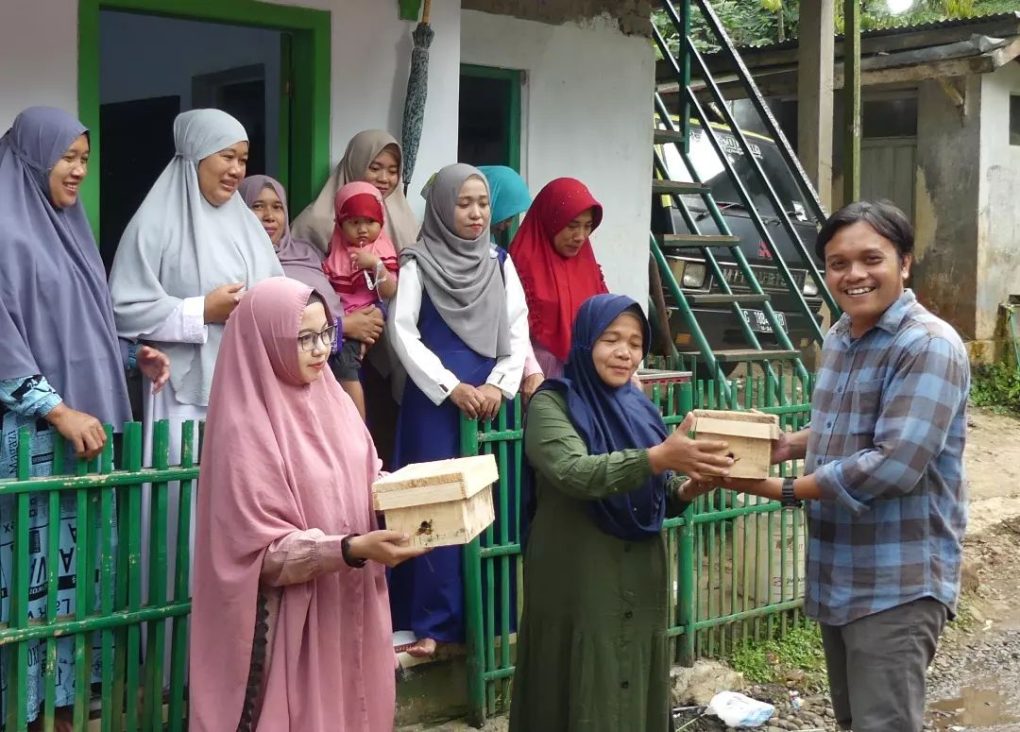
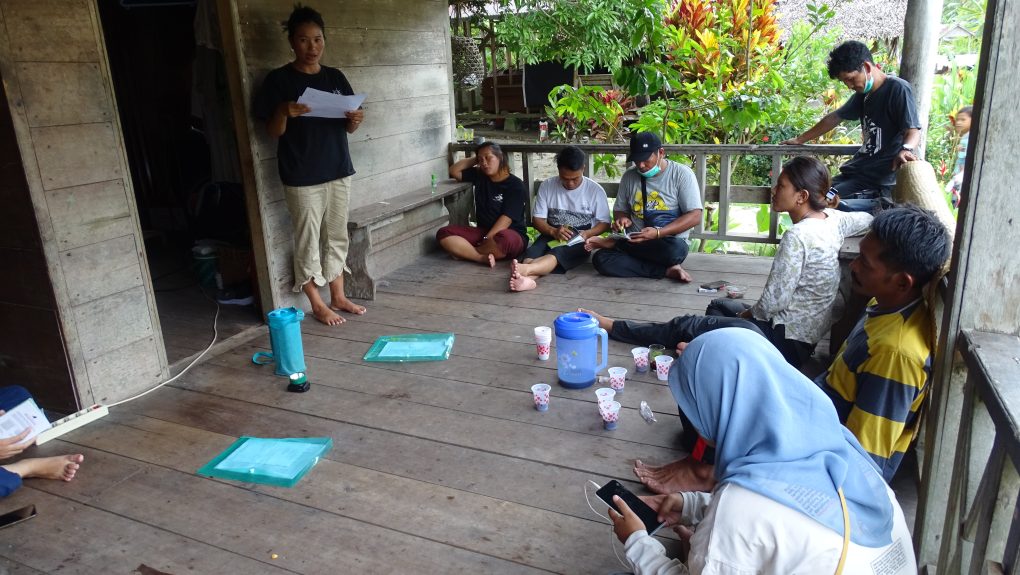
In order to get yet more people in the village interested in the benefits meliponiculture can offer, we collaborated with the Young Farmer Group of Mendolo (PPM) to hold a workshop for women there, who have thus far not been as actively involved in beekeeping as the men. The event took place on 19 August 2022. One of our main selling points is that stingless bees, as suggested by their name, do not sting, and are therefore relatively safe to handle.
We believe that women are key to promoting beekeeping on stinglessbee within the community. Playing an integral role in both raising the next generation and tending to the fields, they are ideally poised to impart new ideas about agriculture and livelihoods to the children and youth of the community. The hope is that they will imbue future generations in Mendolo with the enthusiasm to make meliponiculture a mainstay of the local economy. This has the potential to benefit the village in the following ways:
First, the sale of bee products such as honey can increase family income. If each family keeps enough for their own consumption, the honey could also contribute to their nutrition and enhance their immune systems. This could mean reduced medical expenses in the long run.
Second, beekeeping could make for a more pleasant space to live in. If flowering plants suitable as a food source for bees were integrated into the village design, this would have the added advantage of beautifying both gardens and common spaces. Various types of vegetable crops could be grown for the same purpose, such as chilli and aubergine. With the help of bees pollinating their flowers, farmers could also enjoy increased yields from these crops.
Third, many aspects of bee life can be used to inspire us and educate the next generation. The habit that bees have of storing honey and bee bread, for example, can be used to explain the virtue of saving for a rainy day. We can equally learn from the work ethic of these hardworking insects. Aside from being active all day long, bees have a clear division of labour. A queen bee leads the colony, nurse bees take care of newly hatched bees, guard bees ensure the safety of the hive, and senior worker bees find and gather food.
In the light of all these benefits, we hope that the involvement of Mendolo’s women in meliponiculture can make this and other communities around the gibbon forests more aware of the importance of managing natural resources sustainably, as well as provide them the opportunity to engage in independent entrepreneurship while supporting conservation. Through beekeeping, each community is invited to explore their potential in new and creative ways that foster a healthy planet for future generations.
This beekeeping for women project forms part of the SwaraOwa’s Javan Gibbon conservation programme for 2022-2023, which is supported by Mandai Nature and Fortwayne Childre’s Zoo.
Written by Sidiq Harjanto, Translated by TT. Chan.